HTSQualC: Quality control analysis for high-throughput sequencing data (HTS)
What is HTSQualC?
- HTSQualC is an automated quality control analysis tool for a single and paired-end high-throughput sequencing data (HTS) generated from Illumina sequencing platforms.
- HTSQualC can be used to filter and/or trim sequence reads for low-quality sequences, adapter or primer contamination, and uncalled bases (N) to obtain high-quality data for downstream bioinformatics analysis
HTSQualC Features
- Simultaneously filter and/or trim reads for adapter or primer contamination, uncalled bases (N), and low-quality reads
- Supports single and paired-end reads
- Analyze multiple samples simultaneously
- Parallel computation for accelerating the speed of analysis
- Visualization and statistics
- Docker image is available
- Available on CyVerse Discovery Environment (DE)
- No dependency on an external open-source tool
Getting Started
Prerequisites
HTSQualC requires
- Python 3 (tested on 3.6 and 3.7)
- NumPy
- pysam
- termcolor
- datetime
- matplotlib
Installing
Install using git
# download and install HTSQualC
git clone https://github.com/reneshbedre/HTSQualC.git
cd HTSQualC
python setup.py install
Install using conda,
conda install -c bioconda htseqqc
How to use
Print help message to see all required and optional parameters,
filter.py -h
usage: filter.py [-h] [-a INPUT_FILES_1] [-b INPUT_FILES_2] [-c QUAL_FMT]
[-e N_CONT] [-f ADPT_SEQS] [-d MIN_SIZE] [-g ADPT_MATCH]
[-i QUAL_THRESH] [-n TRIM_OPT] [-p WIND_SIZE]
[-r MIN_LEN_FILT] [-q CPU] [-m OUT_FMT] [-v VIS_OPT]
[--version]
Quality control analysis of single and paired-end sequence data
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-a INPUT_FILES_1, --p1 INPUT_FILES_1
Single end input files or left files for paired-end
data (.fastq, .fq). Multiple sample files must be
separated by comma or space
-b INPUT_FILES_2, --p2 INPUT_FILES_2
Right files for paired-end data (.fastq, .fq).
Multiple files must be separated by comma or space
-c QUAL_FMT, --qfmt QUAL_FMT
Quality value format [1= Illumina 1.8, 2= Illumina
1.3,3= Sanger]. If quality format not provided, it
will automatically detect based on sequence data
-e N_CONT, --nb N_CONT
Filter the reads containing given % of uncalled bases
(N)
-f ADPT_SEQS, --adp ADPT_SEQS
Trim the adapter and truncate the read sequence
(multiple adapter sequences must be separated by
comma)
-d MIN_SIZE, --msz MIN_SIZE
Filter the reads which are lesser than minimum size
-g ADPT_MATCH, --per ADPT_MATCH
Truncate the read sequence if it matches to adapter
sequence equal or more than given percent (0.0-1.0)
[default=0.9]
-i QUAL_THRESH, --qthr QUAL_THRESH
Filter the read sequence if average quality of bases
in reads is lower than threshold (1-40) [default:20]
-n TRIM_OPT, --trim TRIM_OPT
If trim option set to True, the reads with low quality
(as defined by option --qthr) will be trimmed instead
of discarding [True|False] [default: False]
-p WIND_SIZE, --wsz WIND_SIZE
The window size for trimming (5->3) the reads. This
option should always set when -trim option is defined
[default: 5]
-r MIN_LEN_FILT, --mlk MIN_LEN_FILT
Minimum length of the reads to retain after trimming
-q CPU, --cpu CPU Number of CPU [default:2]
-m OUT_FMT, --ofmt OUT_FMT
Output file format (fastq/fasta) [default:fastq]
-v VIS_OPT, --no-vis VIS_OPT
No figures will be produced [True|False]
[default:False]
--version show program's version number and exit
HTSQualC Analysis commands and output
Download the test paired-end dataset (Published in Kandel et al., 2019)
Run HTSQualC on paired-end sequence data,
# once successfully downloaded, use HTSQualC for quality filtering
# with default command and --cpu 6
filter.py --cpu 18 --p1 1_S1_L001_R1_001.fastq --p2 1_S1_L001_R2_001.fastq
# verbose output while program running
# [2020-03-30 21:49:59.738239] The fastq quality format is not provided therefore detecting the fastq variant...
# [2020-03-30 21:50:00.677720] The fastq quality format is illumina 1.8+
# [2020-03-30 21:50:01.618438] Preparing the data for analysis...
# [2020-03-30 21:50:16.445633] Started Filtering of the reads data...
# [2020-03-30 21:54:22.070608] Finished filtering of data successfully...
# [2020-03-30 21:54:22.071288] Output saved in /scratch/user/ren_net/software/HTSQualC/test/1_S1_L001_R1_001_filtering_out
Once the quality control analysis is completed, HTSQualC generates following files for quality evaluations
in the folder 1_S1_L001_R1_001_filtering_out
| Files | Description |
|---|---|
Statistics.txt |
Detailed statistics of quality control evaluations for provided parameters |
1_S1_L001_R1_001_Clean.fastq |
Cleaned sequence data in FASTQ format (left file for paired-end data) |
1_S1_L001_R2_001_Clean.fastq |
Cleaned sequence data in FASTQ format (right file for paired-end data) |
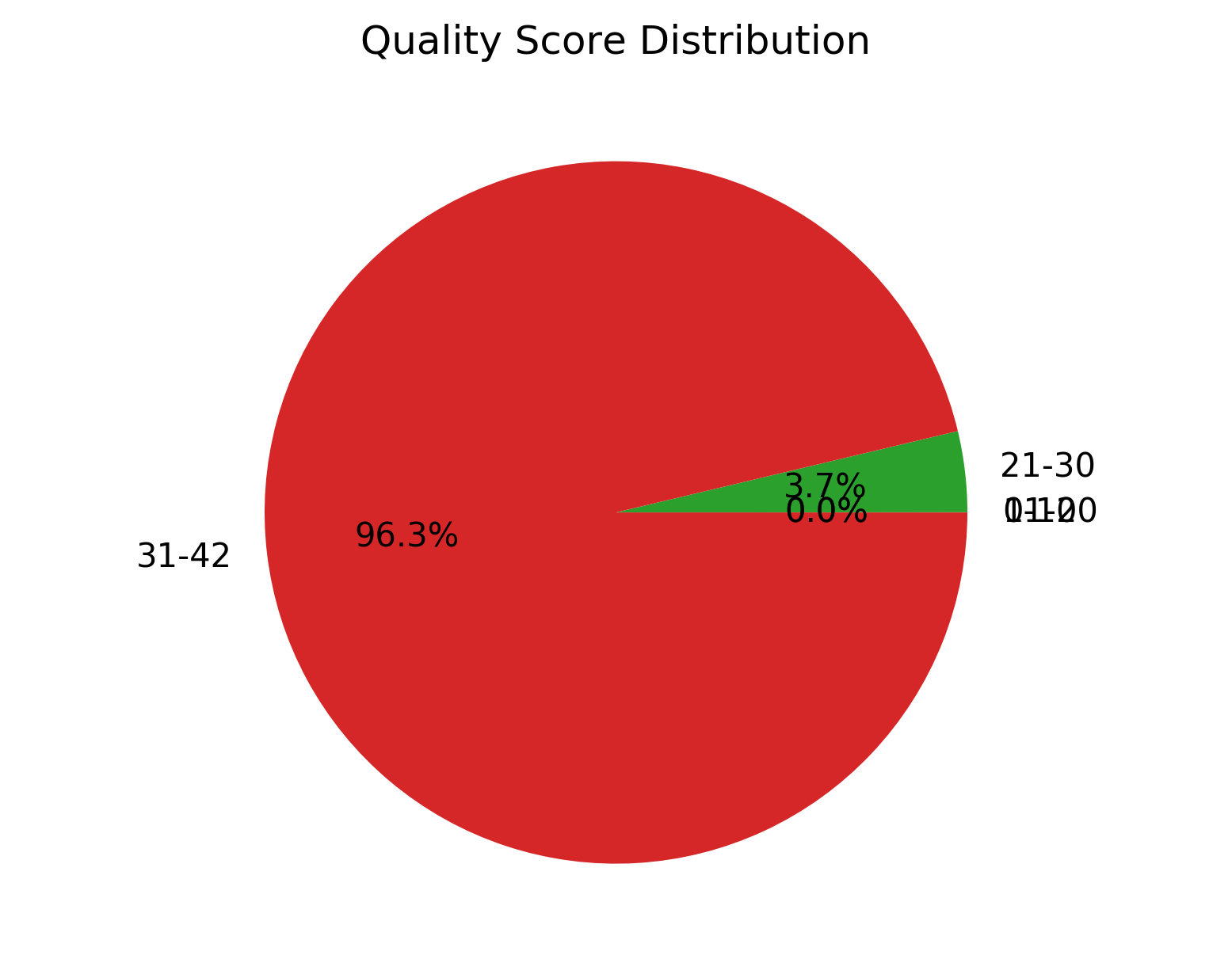
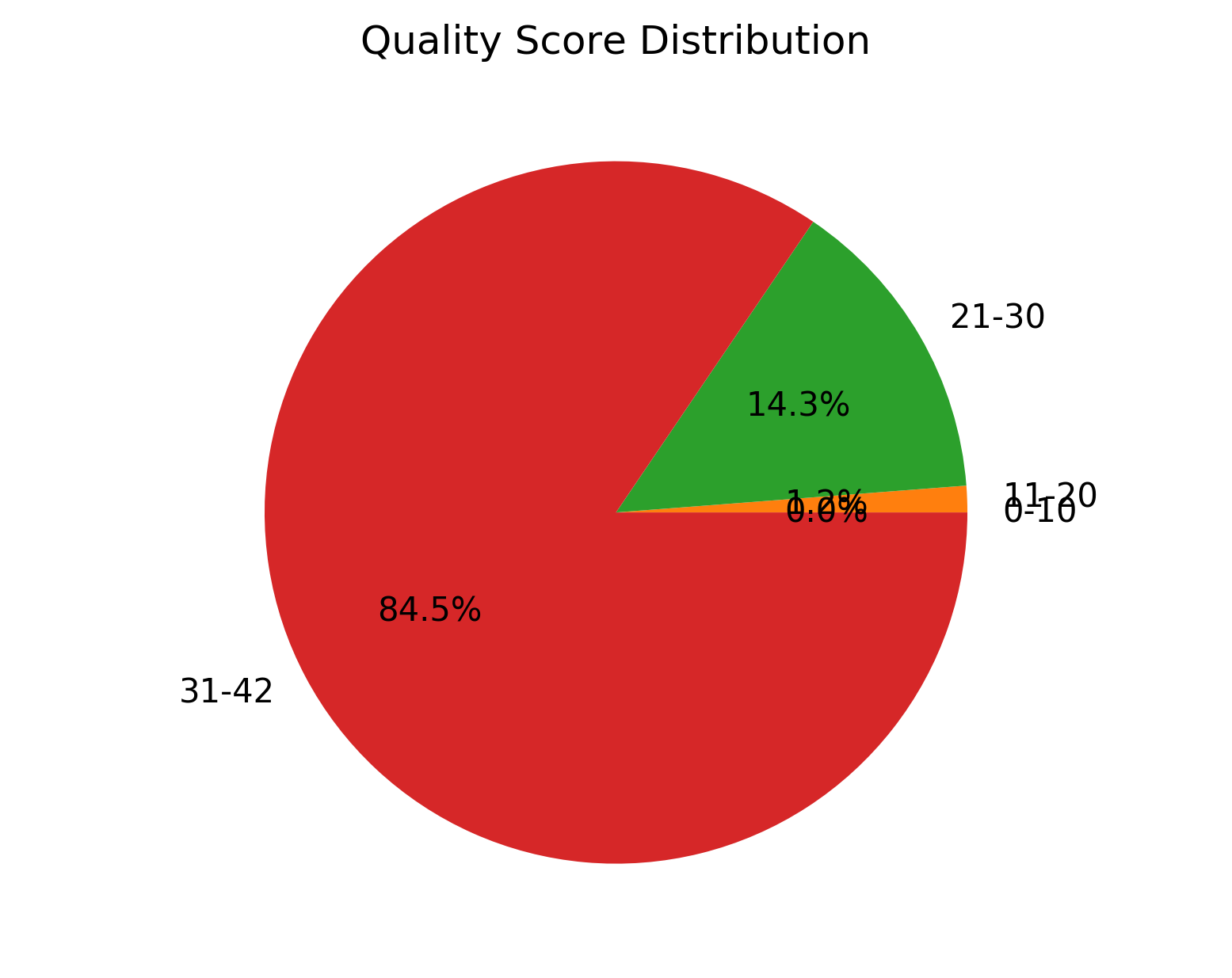
1_S1_L001_R1_001_Qualdist.png |
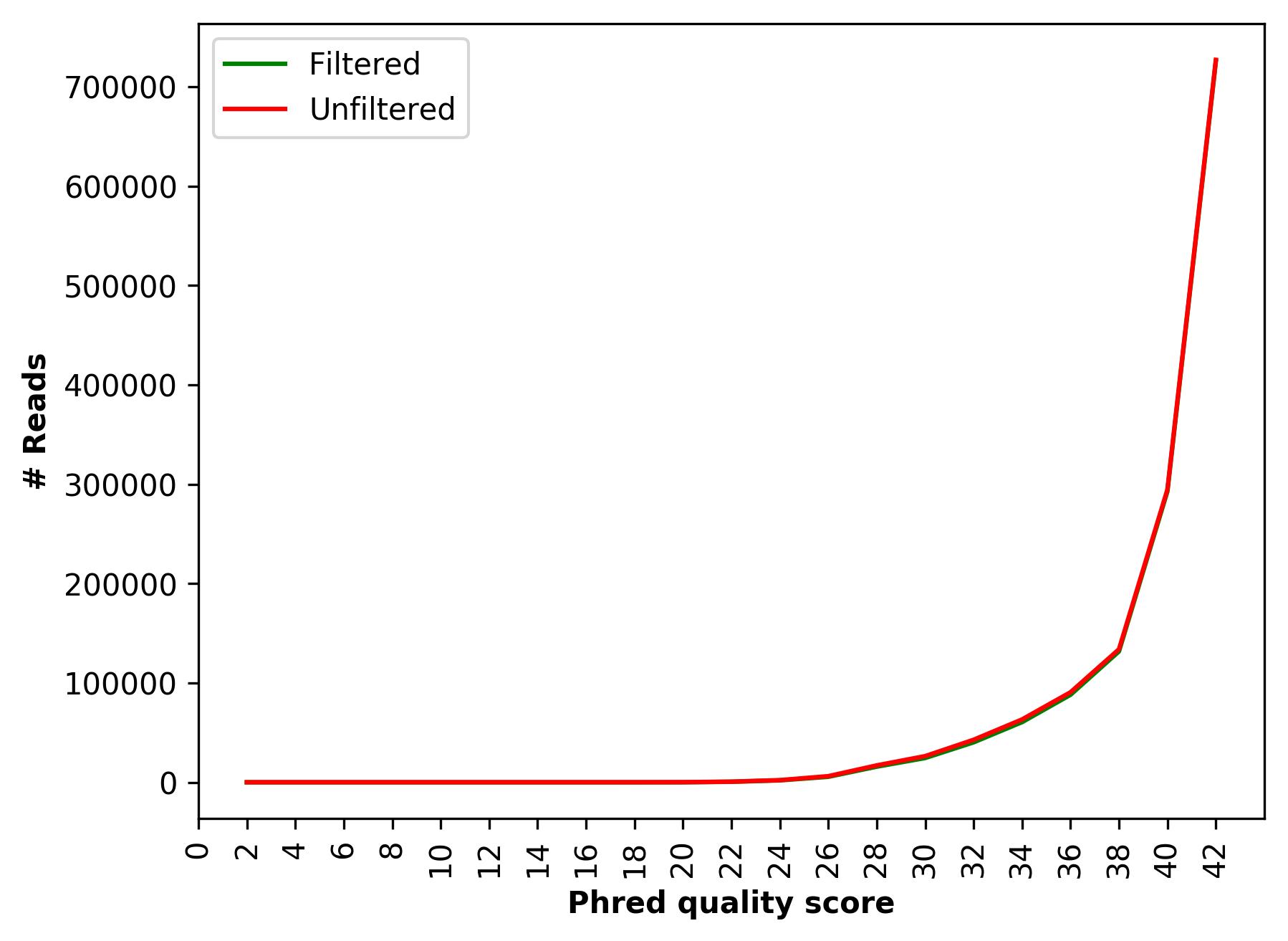
Comparative sequence PHRED quality distribution for raw and cleaned data (for left file) |
1_S1_L001_R2_001_Qualdist.png |
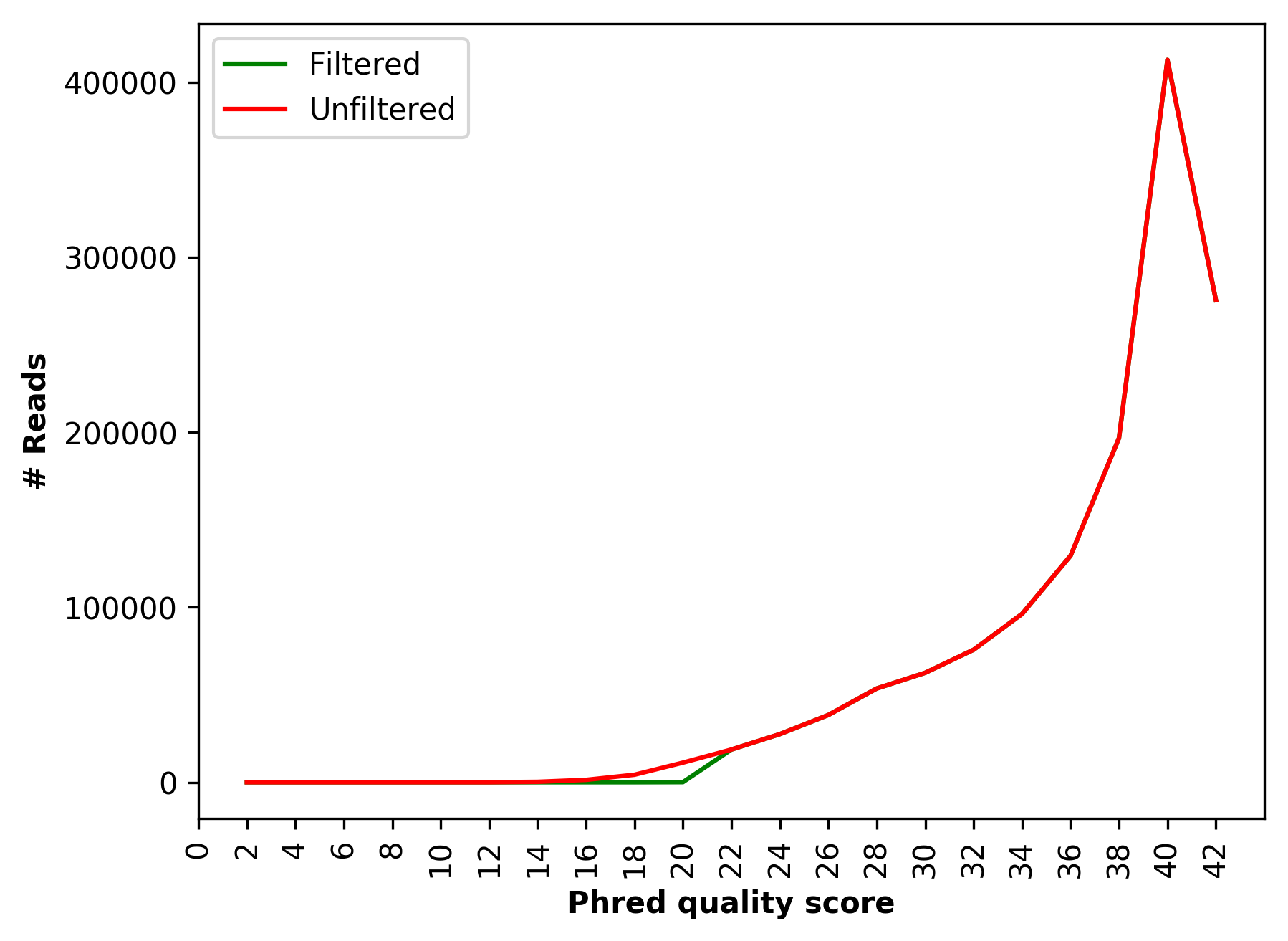
Comparative sequence PHRED quality distribution for raw and cleaned data (for right file) |
1_S1_L001_R1_001_GCdist.png |
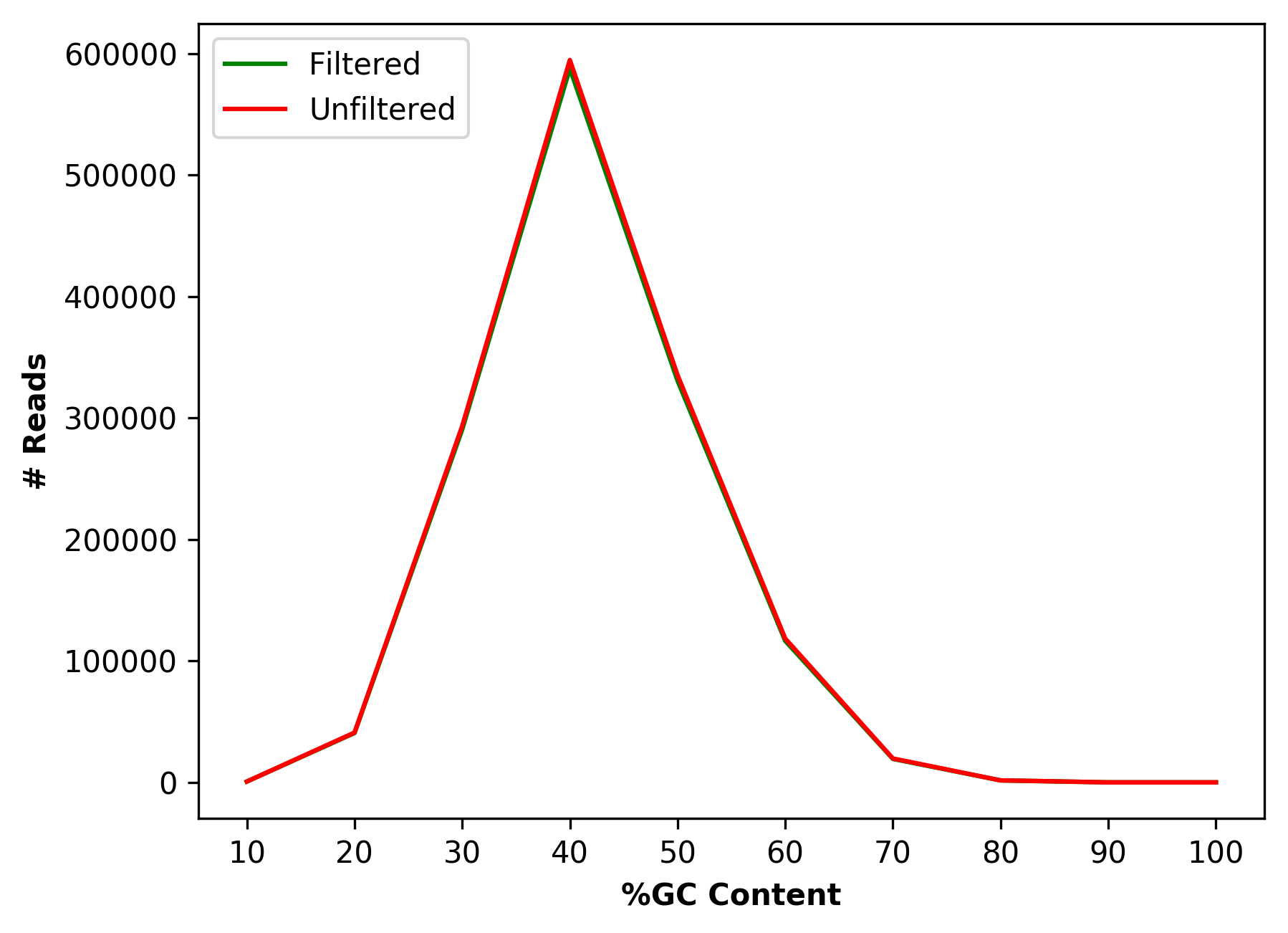
Comparative percentage GC content distribution for raw and cleaned data (for left file) |
1_S1_L001_R2_001_GCdist.png |
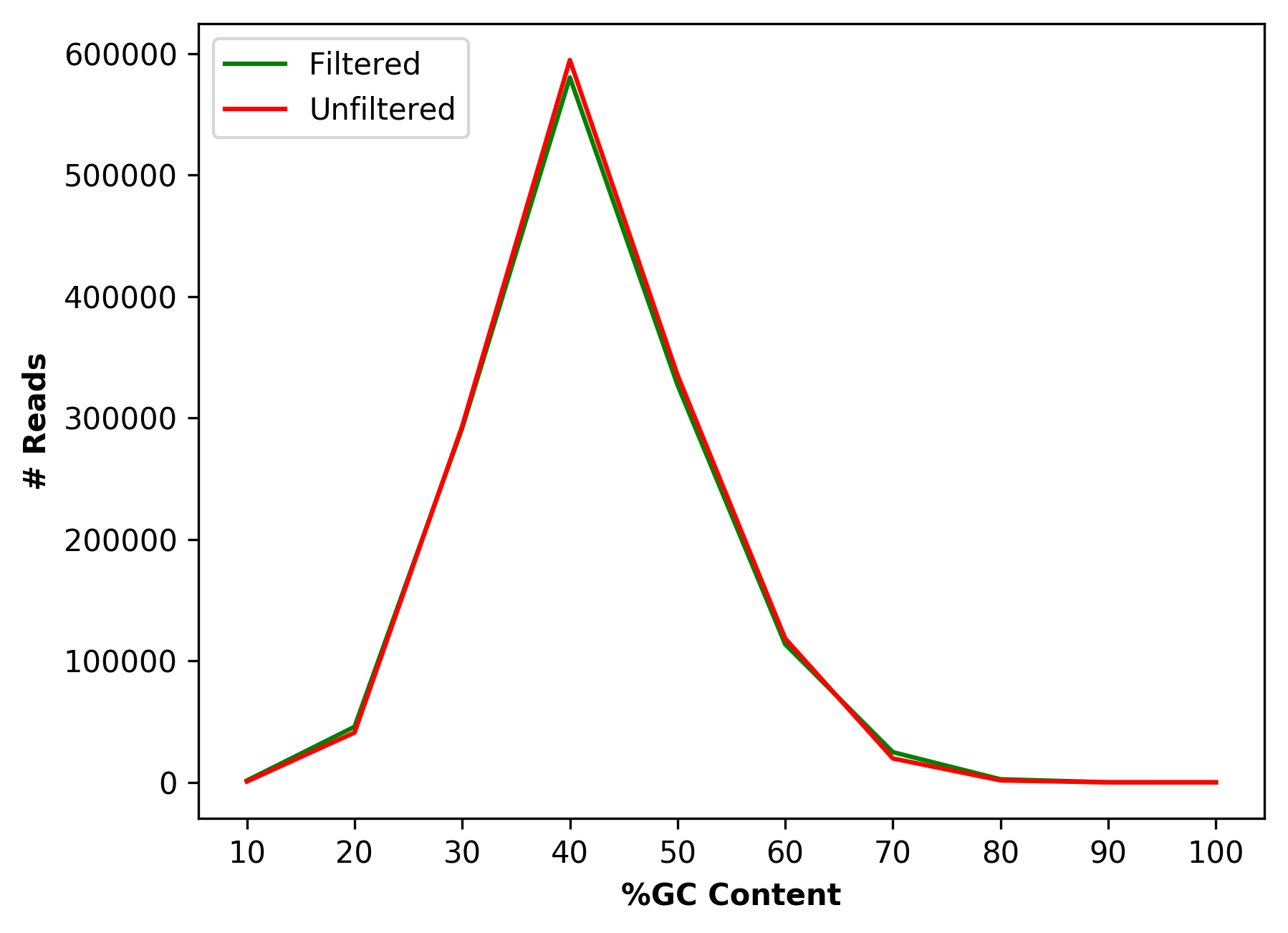
Comparative percentage GC content distribution for raw and cleaned data (for right file) |
1_S1_L001_R1_001_QualGroup.png |
Group-wise sequence PHRED quality distribution for cleaned data (for left file) |
1_S1_L001_R2_001_QualGroup.png |
Group-wise for sequence PHRED quality distribution for cleaned data (for right file) |
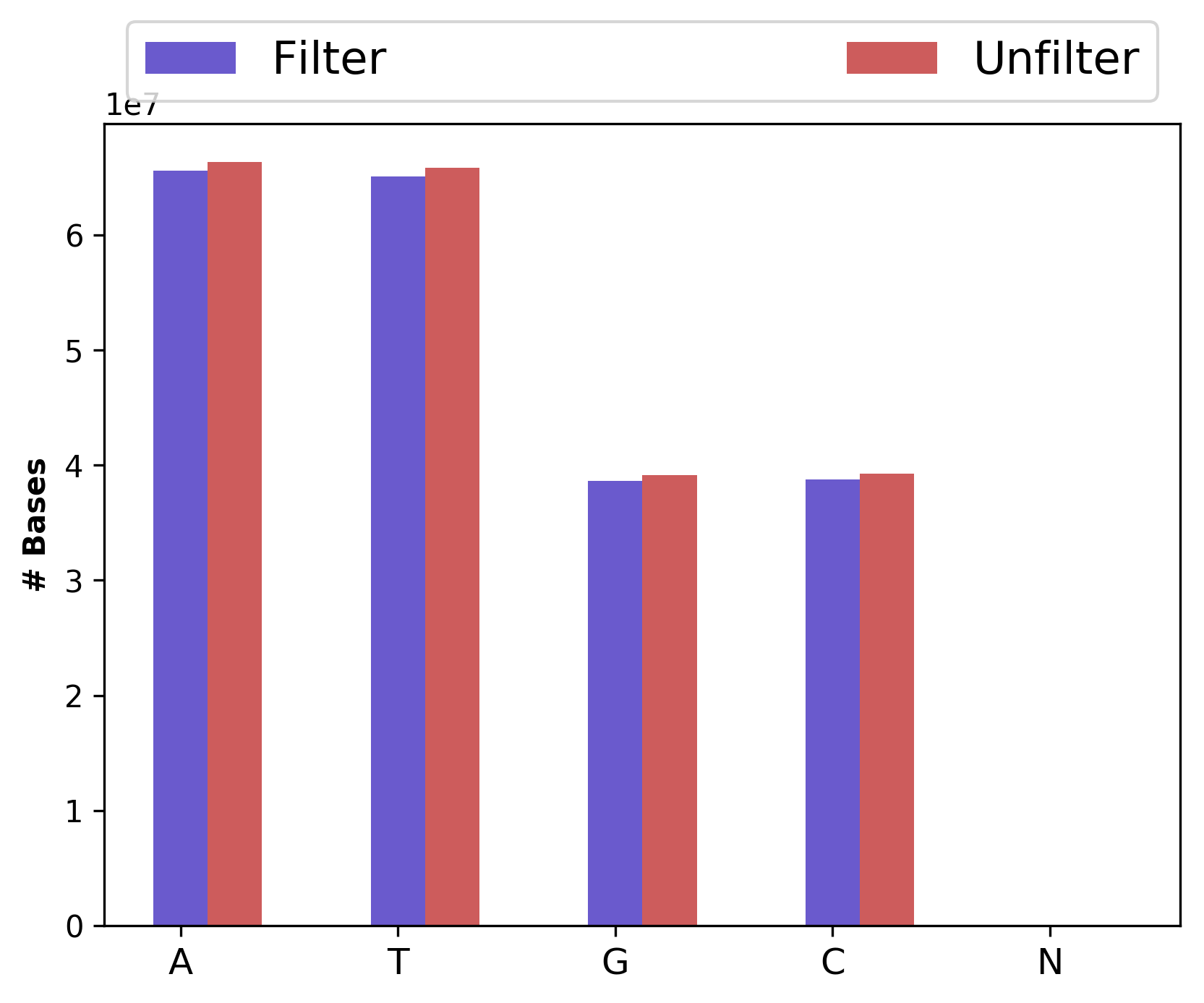
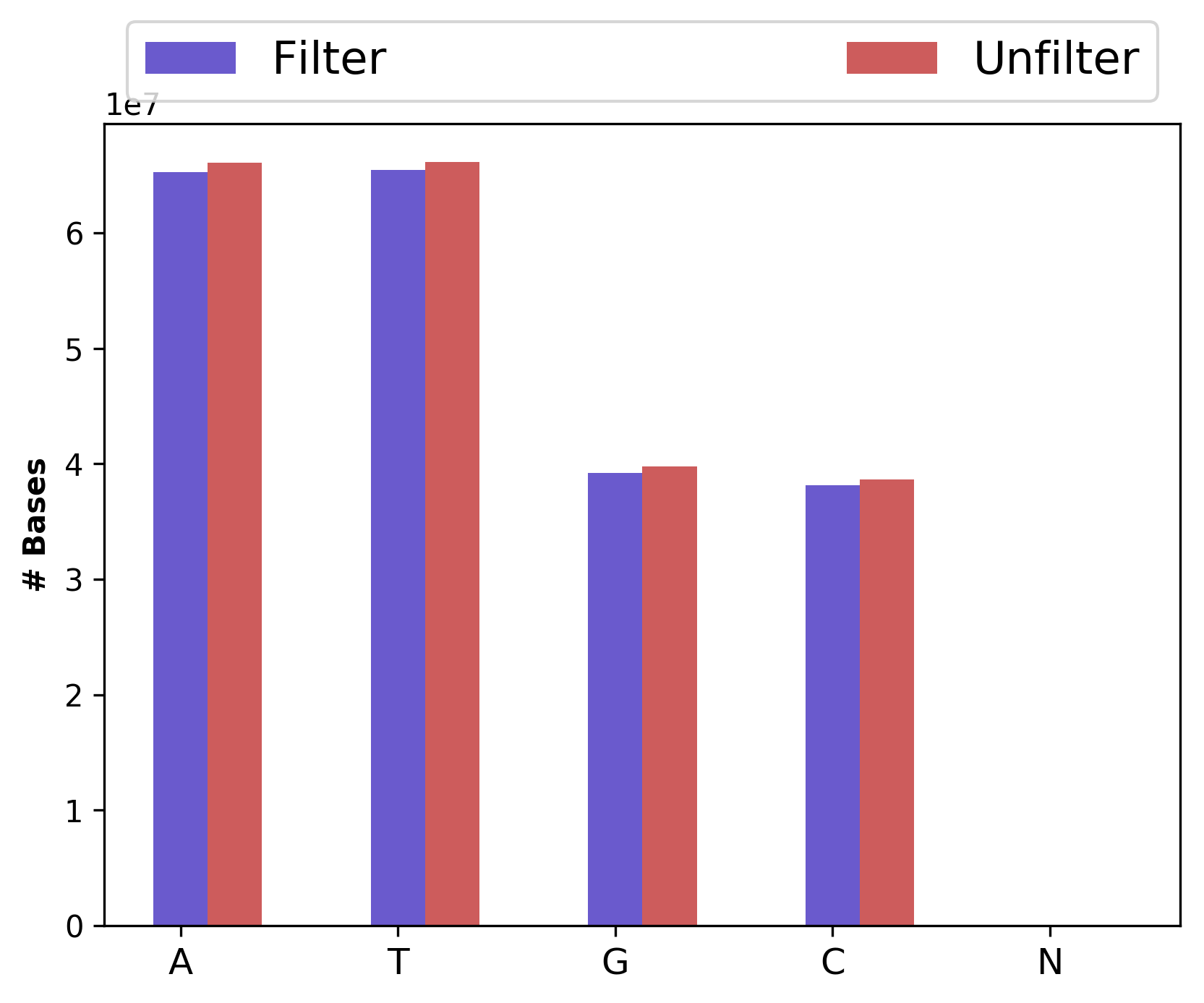
1_S1_L001_R1_001_Basedist.png |
Nucleotide base content for raw and cleaned data (for left file) |
1_S1_L001_R2_001_Basedist.png |
Nucleotide base content for raw and cleaned data (for right file) |
Command.log |
Commands used for the HTSQualC analysis |
Detailed statistics of quality control evaluations (Statistics.txt),
Comparative sequence PHRED quality distribution for raw and cleaned data (1_S1_L001_R1_001_Qualdist.png and
1_S1_L001_R2_001_Qualdist.png),
Comparative percentage GC content distribution for raw and cleaned data (1_S1_L001_R1_001_GCdist.png and
1_S1_L001_R2_001_GCdist.png),
Group-wise sequence PHRED quality distribution for cleaned data (1_S1_L001_R1_001_QualGroup.png and
1_S1_L001_R2_001_QualGroup.png),
Nucleotide base content for raw and cleaned data (1_S1_L001_R1_001_Basedist.png and
1_S1_L001_R2_001_Basedist.png),
Run HTSQualC by changing the parameters for different quality thresholds, adapters, and uncalled bases content.
All parameters can be checked using filter.py -h
# for paired end data with quality threshold, adapter sequences, and uncalled based parameters
filter.py --cpu 18 --qthr 25 --nb 5 --adp AGATCGGAAGAGCACACGTCTGAACTCCAGTCA,AGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGTGT
--p1 1_S1_L001_R1_001.fastq --p2 1_S1_L001_R2_001.fastq
Run HTSQualC for multiple files simultaneously
# for paired end data with default parameter and multiple samples
filter.py --cpu 18 --p1 1_S1_L001_R1_001.fastq,2_S1_L001_R1_001.fastq,3_S1_L001_R1_001.fastq
--p2 1_S1_L001_R2_001.fastq,2_S1_L001_R2_001.fastq,3_S1_L001_R2_001.fastq
# Note: 2 and 3 files are not provided with datatsets. These are provided in commands
# for illustration purpose only
Similarly, HTSQualC can be used for running single-end datasets (just exclude --p2 parameter)
Run HTSQualC using Nextflow
- Nextflow can also be used to run HTSQualC
analysis. HTSQualC package also comes with Netxflow template (
nextflow_template.nf) for running the analysis - If you have not installed Nextflow, you can install it as
curl -s https://get.nextflow.io | bash. Nextflow works best withjavaversion between 8 to 12. You can check the currentjavaversion asjava -version - HTSQualC can be used to run multiples files by providing each file name explicitly in the command line. Nextflow can automate this process by providing file patterns and thus avoiding providing each file name to HTSQualC.
- You can also run nextflow with distributed computing (run on several computing nodes) on high-performance
computers (using
mpirun) - For example, if you have three paired-end files (total 6
FASTQfiles) with filename ending pattern ofR1_001.fastqR2_001.fastq(check above HTSQualC for multiple files commands), then you can edit the nextflow template like below,
// input data directory path
DATAP = "/scratch/user/ren_net/software/HTSQualC/test"
// input file extension
FileExtension="fastq"
// Check paired end files (for single end files remove 2)
// first should check the file name structure before using
allReads="${DATAP}/*_{R1_001.fastq,R2_001.fastq}.${FileExtension}"
log.info """\
HTSQualC Quality Filtering
=============================
reads : ${DATAP}
"""
.stripIndent()
// for paired end reads
Channel
.fromFilePairs(allReads)
.ifEmpty { error "Cannot find any reads matching: ${DATAP}" }
.set { read_pairs }
// filter data
process filterData {
tag "$pair_id"
input:
set pair_id, file(reads) from read_pairs
script:
"""
# you can change HTSQualC parameter here
filter.py --cpu 18 --p1 ${reads[0]} --p2 ${reads[1]}
"""
}
Once you edit the nextflow template file, run it as
./nextflow nextflow_template.nf
Once nextflow run is completed, you can see the output files in the work directory generated
in the same directory
Run HTSQualC as GUI using CyVerse
Check detailed documentation here
How to cite:
- Bedre R, Rajasekaran K, Mangu VR, Timm LE, Bhatnagar D, Baisakh N. Genome-wide transcriptome analysis of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) identifies candidate gene signatures in response to aflatoxin producing fungus Aspergillus flavus. PLoS One. 2015;10(9).
- Bedre R, Irigoyen S, Schaker PD, Monteiro-Vitorello CB, Da Silva JA, Mandadi KK. Genome-wide alternative splicing landscapes modulated by biotrophic sugarcane smut pathogen. Scientific reports. 2019 Jun 20;9(1):1-2.
- Renesh Bedre. HTSQualC: Quality control analysis for high-throughput sequencing data (HTS). https://reneshbedre.github.io/blog/htseqqc.html
Last updated: July 21, 2021
